Getting PowerShell Script Block Logging events with context like who, when, and how run the code
Recently we've enabled the PowerShell Script Block logging security feature in our environment to be able to see what PowerShell commands were run on our computers. But what was my surprise when I found out there is no easy way to get such events with some context like who run such command, how the console was invoked when it started/ended etc.
So I've created a function Get-PSHScriptBlockLoggingEvent to solve this issue 🙂
What is PowerShell Script Block logging?
There are already a lot of good articles about PowerShell Script Block logging feature, but in a nutshell:
it is available since PowerShell v5
allows you to log every command run on your host in PSH 5.x, 6.x or 7.x
events with ID 4104 are logged into the special
Microsoft-Windows-PowerShell/Operational(for Windows PowerShell) orPowerShellCore/Operational(for PowerShell Core) event logs and contain deobfuscated dataevents can be encrypted using a certificate, so you don't have to worry about leaking sensitive data
TL;DR
Install the newest version of my module
CommonStuffand call functionGet-PSHScriptBlockLoggingEventInstall-Module CommonStuff -force Import-Module CommonStuff # get Script Block logging events with all possible details for last 24 hours Get-PSHScriptBlockLoggingEvent
Retrieval of Script Block logging events
The simplest way to get Script Block logging events (ID 4104) looks like this 👇
# for Windows PowerShell
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{logname = "Microsoft-Windows-PowerShell/Operational"; id = 4104 } | select -ExpandProperty message
# for PowerShell Core
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{logname = "PowerShellCore/Operational"; id = 4104 } | select -ExpandProperty message
And the result can be like 👇
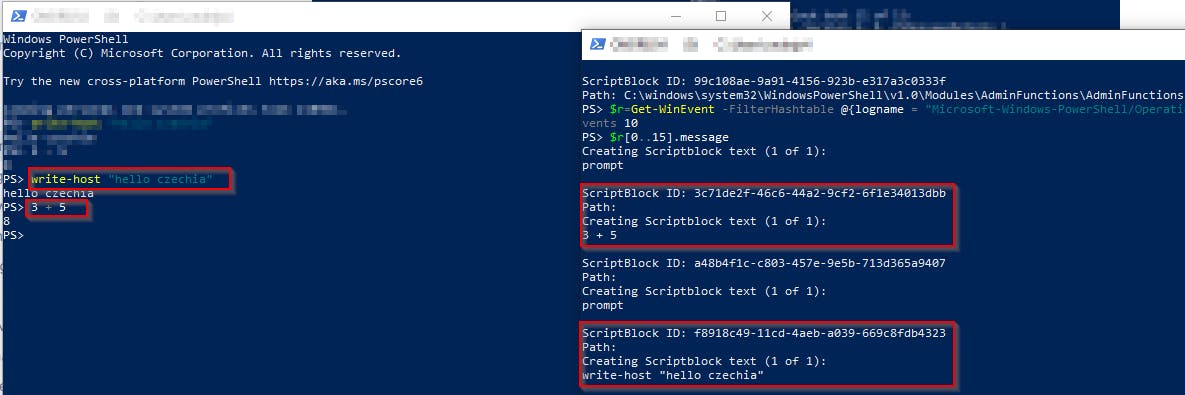
As you can see the returned result contains nothing more than invoked commands. The commands text is split into several events and contains not just the command text itself, but also some additional data that has to be cut off.
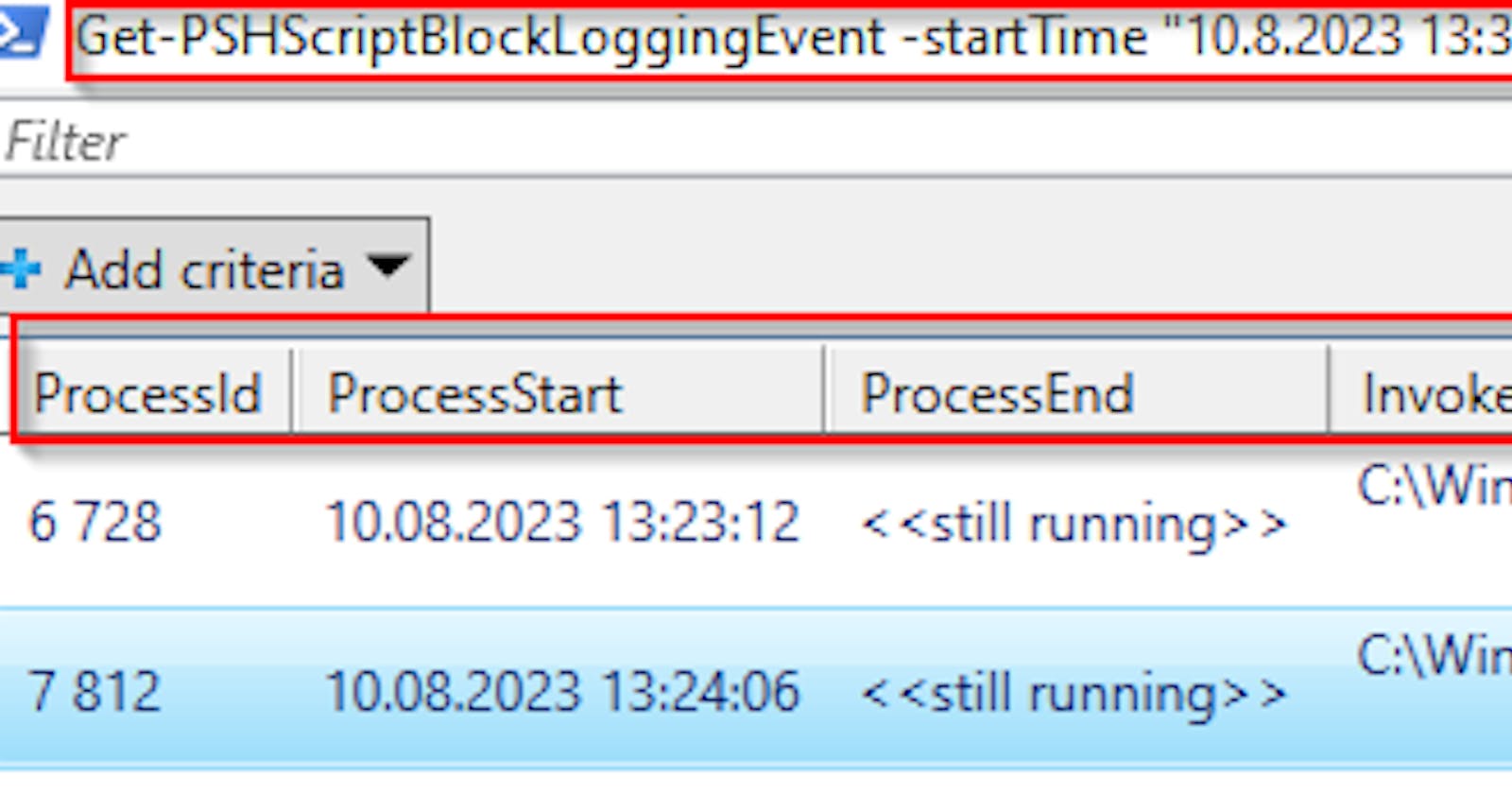
Now compare it with the result returned via my function Get-PSHScriptBlockLoggingEvent 👇
Get-PSHScriptBlockLoggingEvent -startTime "10.3.2023 13:35" | Out-GridView

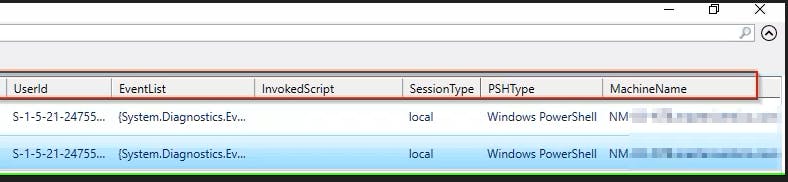
Run commands are grouped by PSH console ProcessId and a lot of additional data are shown.
Advantages of my Get-PSHScriptBlockLoggingEvent function
Supports reading of
Both
Windows PowerShellandPowerShell Coreevent logsLocal computer event logs
Remote computer event logs (as a path to exported evtx files)
Forwarded event log (on event collector machine)
Among commands that were run, returns context like
When the PSH process started/ended
How the PSH process was invoked
Who invoked the PSH process
What scripts were invoked during the session
Type of the session (local/remote)
Type of the PSH console (Windows PowerShell/PowerShell Core)
Computer name where commands were run
Checks included
Required event logs are enabled
Script Block Logging is enabled
Certificate with a private key is available (in case Protected Event logging is enabled)
Event logging manifest is enabled (if PowerShell Core is detected)
...
Offers option to enable Script Block logging if it is not enabled already
What event logs are used to get the context
To be able to show the context of the command, Get-PSHScriptBlockLoggingEvent function combines data from several event logs:
Microsoft-Windows-PowerShell/Operational (for Windows PowerShell) and PowerShellCore/Operational (for PowerShell Core)
4104 event
- contain content of the invoked commands
40961 event
- contain start time of the invoked PSH session
Microsoft-Windows-WinRM/Operational
91 event
- contain start time of the session, by who and from which host it was started
Windows PowerShell (data only for Windows PowerShell)
400 event
- contain details about how the session was invoked and by whom (is logged a few milliseconds (or seconds :D) after the 40961 event)
403 event
- contain when the session ended and can be found through (correlates with 400 event through HostId value)
What obstacles had to be solved?
There is no unique identifier that can be used to correlate all PowerShell-related events!
4104 and 40961 events contain ProcessId, but start/stop events (400) don't
To get the corresponding start event (400), you have to find the closest one (by comparing
CreateTimeproperty)- Sometimes these are created exactly at the same time
To get stop event (403), you need
HostIdproperty which is the same as for the start event (400)
The PowerShell start event (400) is sometimes not logged at all for some reason
ProcessId is surprisingly often reused which complicates the grouping of the events from one session
TIPs
How Script Block logging can be bypassed?
As an administrator delete the registry value
EnableScriptBlockLoggingsaved inHKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ScriptBlockLogging(for Windows PowerShell)HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\PowerShellCore\ScriptBlockLogging(for PowerShell Core 6.x)HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\PowerShellCore\ScriptBlockLogging(for PowerShell Core 7.x)
And start a new PowerShell console (the old one will be still logged!)
Use PowerShell 2.0 if it is enabled in the system (by default it is)
Use PowerShell Core without registering "
Windows Event Logging Manifest" during the installation a.k.a. don't create PowerShell Core event log
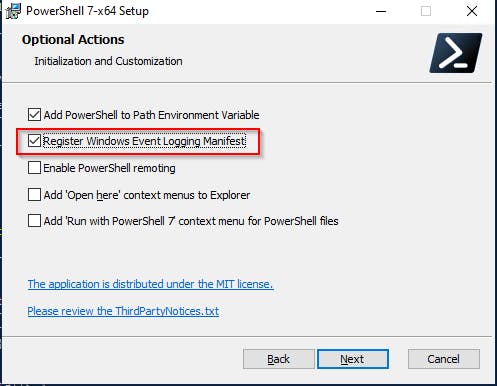
As an administrator clear the following event logs (this won't help if they are forwarded to some SIEM in the realtime though) or (probably a better solution) is to disable them
Microsoft-Windows-PowerShell/OperationalPowerShellCore/OperationalWindows PowerShell(cannot be disabled)Microsoft-Windows-WinRM/Operational
How certificate for Protected Event Logging (PEL) can be created?
Save the following text into the
PEL.inffile (encoded as UTF8!).You can edit
SubjectandValidityPeriodUnitsparts as you like[Version] Signature = "$Windows NT$" [Strings] szOID_ENHANCED_KEY_USAGE = "2.5.29.37" szOID_DOCUMENT_ENCRYPTION = "1.3.6.1.4.1.311.80.1" [NewRequest] Subject = "cn=PEL@contoso.com" MachineKeySet = false KeyLength = 4096 KeySpec = AT_KEYEXCHANGE HashAlgorithm = Sha256 Exportable = true RequestType = Cert KeyUsage = "CERT_KEY_ENCIPHERMENT_KEY_USAGE | CERT_DATA_ENCIPHERMENT_KEY_USAGE" ValidityPeriod = "Years" ValidityPeriodUnits = "1000" [Extensions] %szOID_ENHANCED_KEY_USAGE% = "{text}%szOID_DOCUMENT_ENCRYPTION%"
In the working directory where
PEL.infis stored openCommand Promptand call the following commandcertreq -new PEL.inf PEL.cerA new certificate
PEL.cerwill be created in the working directory and also in your Certificate Personal storeExport the newly created certificate from your certificate store (including the private key!) as
PEL.pfx
PEL.cercan be used for events content encrypting,PEL.pfxfor decryptingOfficial tutorial for enabling PEL